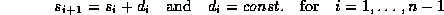 is defined formally as a sequence of data quanta
is defined formally as a sequence of data quanta  contributed by the single-medium substreams
contributed by the single-medium substreams 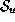 to the multimedia stream M:
to the multimedia stream M:





The information that can be perceived by the human senses is transported through different media, such as text or sound. Humans communicate with computers by means of various media, or use computers as tools for communication with each other. These observations led Steinmetz to the following definition of multimedia systems [HS91]:
``A multimedia system is characterised by the computer-controlled generation, manipulation, presentation, storage, and communication of independent discrete and continuous media.''The ability to handle continuous media, such as audio or video, distinguishes multimedia systems from most conventional computer systems. Continuous media, while being actually discrete, appear smooth to the human observer when presented regularly and periodically at sufficiently high frequencies. Therefore, continuous media are time dependent, and their processing is subject to time constraints.
A good way to describe the propagation of continuous media data through a system or over a network is the
stream metaphor: a sequence of data units flows from sources to sinks along
the data path.
A set of related data substreams, each carrying one particular continuous medium,
forms a multimedia data stream. Following Husemann [Hus96, p. 20,],
a multimedia data stream 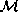 is defined formally as a sequence of data quanta
is defined formally as a sequence of data quanta  contributed by the single-medium substreams
contributed by the single-medium substreams 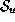 to the multimedia stream M:
to the multimedia stream M:
Most research into the modelling of multimedia data is done in the context of
multimedia database systems. Gibbs et
al. [GBT93] also consider database issues, but focus on the time aspects of multimedia
data.
Gibbs et
al. [GBT93] also consider database issues, but focus on the time aspects of multimedia
data.
Their investigation into the time constraints of multimedia data
streams caused the authors to develop the notion of timed streams.
A timed stream consists of a finite sequence of tuples
consists of a finite sequence of tuples 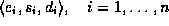 . All
. All
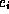 are media elements
are media elements of a certain media type. The media type is characteristic for the
stream and specifies the attributes of the medium of the stream.
of a certain media type. The media type is characteristic for the
stream and specifies the attributes of the medium of the stream. 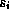 and
and 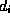 are
measured in a discrete time system and specify the time constraints of the
presentation of
are
measured in a discrete time system and specify the time constraints of the
presentation of 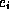 :
: 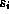 is the start time of the presentation of
is the start time of the presentation of 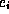 , and
, and 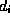 is the
duration of the presentation.
is the
duration of the presentation.
Consider for example a fixed--frame-rate MPEG video stream: the
individual video frames could be identified as the media elements 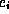 , whose size can vary,
depending on the MPEG type of each frame
, whose size can vary,
depending on the MPEG type of each frame 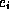 ; because of the constant frame rate, the
; because of the constant frame rate, the 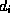 would be equal for all i; furthermore, the end of the duration of the presentation of element
would be equal for all i; furthermore, the end of the duration of the presentation of element
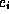 would coincide with the beginning of the presentation of the next element
would coincide with the beginning of the presentation of the next element 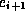 ,
formally
,
formally