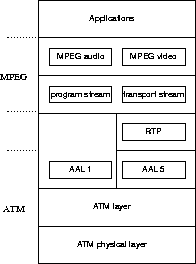
Figure: A video-on-demand protocol stack.





No standards for home video-on-demand distribution networks have been accepted yet. While the backbone of a video-on-demand network would probably be based on ATM and/or SONET, more and differing techniques have been proposed by telephone, cable TV, and other companies for the local distribution. Tanenbaum [Tan96, p. 750--753,] identifies the four most important approaches as:
 shows a potential stack, comprising ATM and its sublayers, potentially RTP,
MPEG and its layers, and applications on top.
shows a potential stack, comprising ATM and its sublayers, potentially RTP,
MPEG and its layers, and applications on top.

Figure: A video-on-demand protocol stack.
The Internet community is also developing mechanisms and protocols that allow the integration of media
servers in multimedia sessions. The IETF MMUSIC working group for example is working on the
Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP').
This is an application-level text-based protocol intended to control the delivery and recording of real-time
data.
Its tasks comprise the choice of delivery channels---such as (multicast) UDP and TCP---and delivery
mechanisms based on RTP, the exchange of session descriptions, and the control of data streams by commands
such as PLAY, RECORD, or STOP.
RTSP' is capable of controlling multiple delivery sessions at once, which can include both live-fed and
stored media clips.
Session descriptions, encoded for example in the SDP format, are retrieved from a web server or the media
server itself, typically using HTTP. Each media stream listed in a session description is identified by
an RTSP URL, which points to a media server that provides the particular stream.




